Copyright medicaldialogues
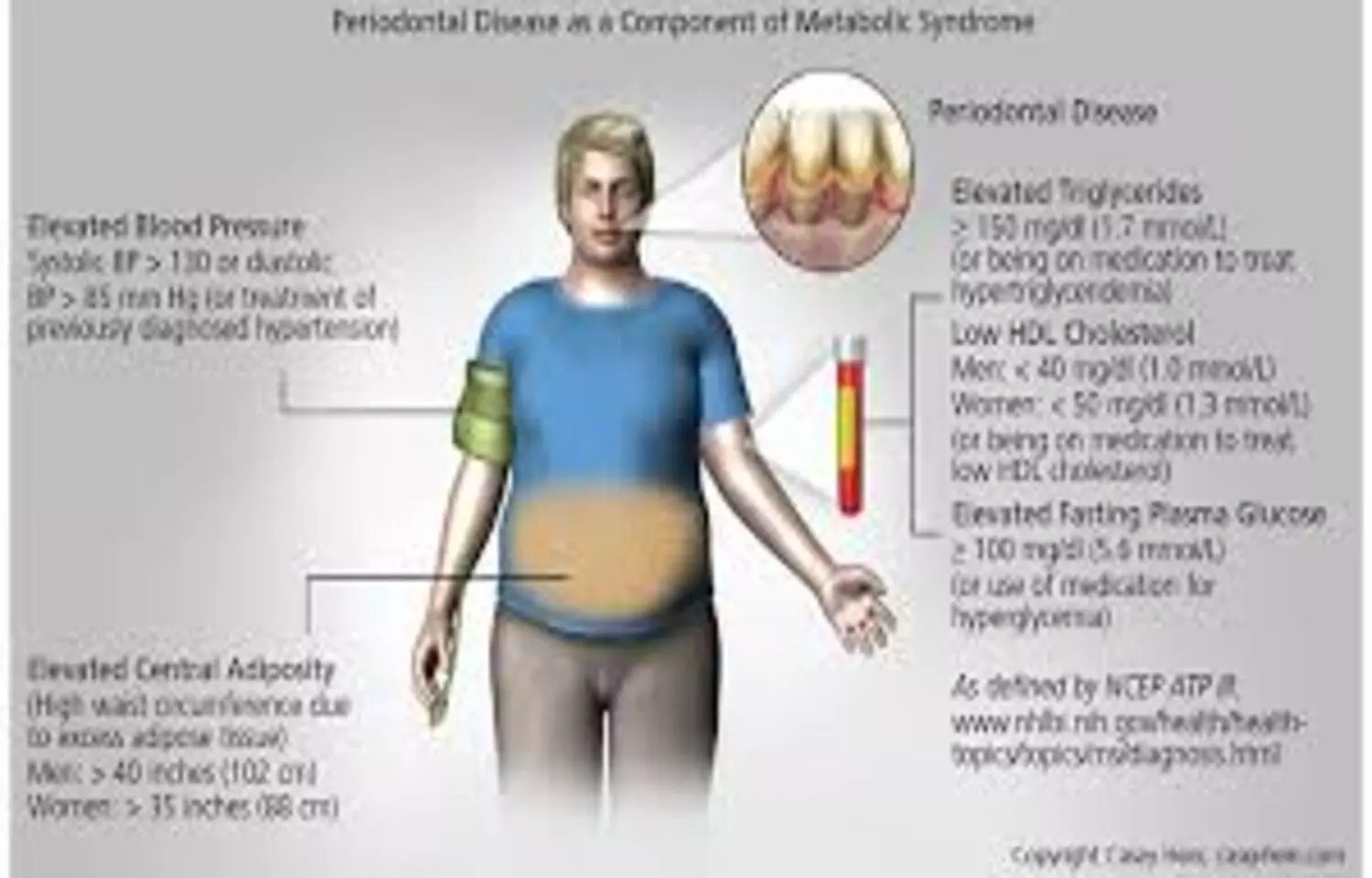
A new study published in Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease reports that obesity, assessed through body mass index (BMI) and central adiposity measures, is independently associated with greater severity of periodontitis. The findings highlight growing evidence that excess body fat can worsen inflammatory gum disease and should be considered a key risk factor in periodontal health assessments.The cross-sectional study, led by Soumya Vishwanath and colleagues, explored the connection between obesity indicators and periodontal status in adults. Researchers found that individuals with higher BMI, waist circumference, and waist-to-hip ratio showed significantly more attachment loss, deeper periodontal pockets, and higher bleeding indices compared with participants of normal weight. These associations remained statistically significant even after adjusting for age, gender, smoking habits, and socioeconomic factors.Periodontitis is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects the tissues supporting the teeth. It has been increasingly linked with systemic inflammatory conditions such as diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The authors noted that obesity contributes to a pro-inflammatory state through the release of adipokines and cytokines from adipose tissue, which may intensify periodontal tissue destruction. This mechanism explains why obese individuals may experience more rapid progression of gum disease and poorer treatment outcomes. The study underscores the importance of assessing obesity when estimating periodontal risk. The authors recommend that dental and medical professionals adopt an integrated approach that includes monitoring BMI and waist measures during periodontal evaluation. They suggest that lifestyle interventions targeting weight reduction and metabolic balance could support better periodontal health outcomes alongside standard dental therapy. By confirming obesity as an independent predictor of periodontitis severity, the research reinforces the close interplay between oral and systemic health. Recognizing and managing obesity not only benefits overall metabolic health but may also reduce the risk of chronic gum inflammation, tooth loss, and associated systemic complications.Reference:Vishwanath S, Gurumurthy V, Saini RS, et al. The impact of body mass index on periodontitis: a cross-sectional study. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease. 2025;16. doi:10.1177/20406223251383319Keywords: obesity, periodontitis, BMI, oral inflammation, periodontal disease, metabolic health, adipokines, chronic disease