Copyright newsbytesapp

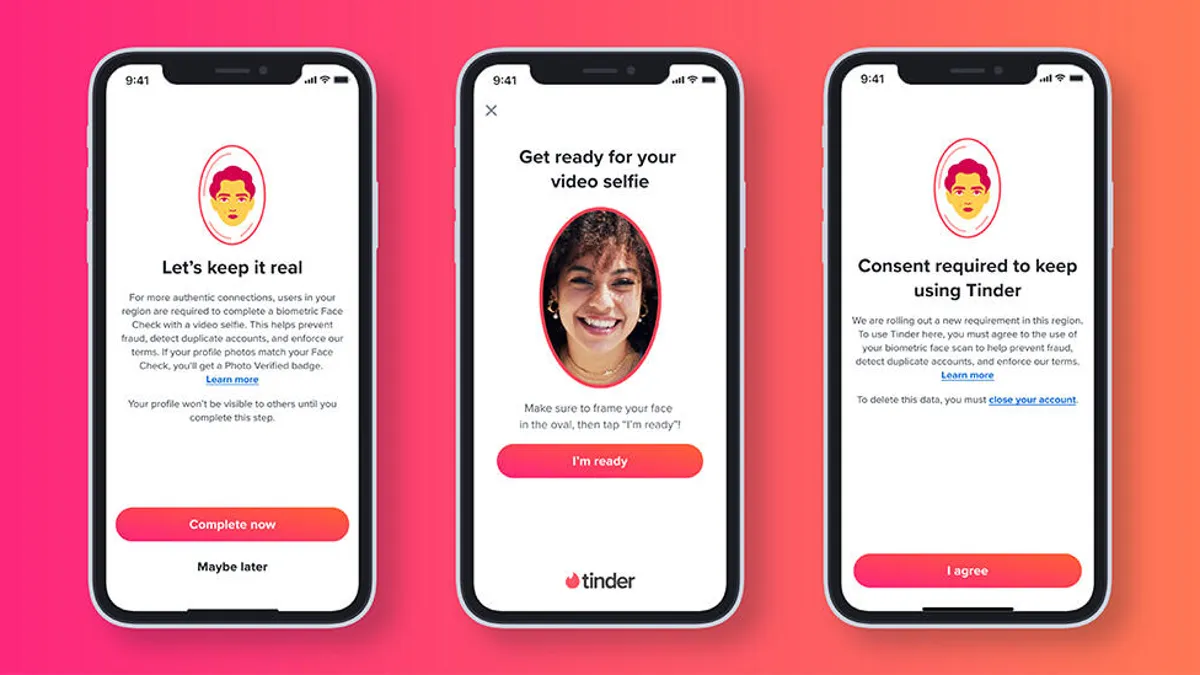
CAPTCHAs, or Completely Automated Public Turing tests to tell Computers and Humans Apart, were once a common sight on the internet. These puzzles were designed to keep bots out by presenting users with distorted text or image grids to identify. However, in recent years, these challenges have become increasingly bizarre and rare. Now you might be wondering why this shift has happened. When CAPTCHA was first invented (in 2003), the idea was simple: present a task that computers couldn't parse (like warped text) but humans could read. The first CAPTCHAs were used by companies like PayPal and Yahoo to keep automated bots at bay. Over time, as AI improved, security systems hardened the puzzles with image grids, object selection, and more. As online security challenges became more complex, users also grew frustrated with these increasingly bizarre questions. In 2007, reCAPTCHA was introduced to have users identify words that machine learning algorithms couldn't read at the time. Google acquired this technology and used it for digitizing books. In 2018, the tech giant launched reCAPTCHA v3. This invisble CAPTCHA was a major shift toward reducing the frequency of these challenges. Rather than interrupting you with tests, these systems continuously monitor your on-page behavior—cursor movement, clicks, typing speed—to assign a risk score. Humans passed seamlessly while bots were blocked. In 2022, Cloudflare launched Turnstile, a reCAPTCHA alternative that uses pattern-based usage analysis instead of human-completed tests. Like the standard reCAPTCHA, Turnstile can be added to websites for free. You may not recognize the name, but you've likely seen it: Click box to prove you're human. Clicking the button doesn't automatically mean you pass, says Reid Tatoris, who leads Cloudflare's application security detection team. The system collects data from your device and software before deciding whether to grant access. Still, a few CAPTCHAs remain, and those tend to be strange. Security firms are increasingly using cost-proofing strategies—puzzles that are not impossible for bots but make attacks economically unviable. For example, Arkose Labs's MatchKey may show a collage with no real-world equivalent or a slide puzzle that AI has never encountered. The goal is to raise the bar by making attacks too costly in time or computing resources to attempt. For users, the shift from CAPTCHA is mostly invisible—fewer interruptions, fewer annoying broken puzzles. But it also means that more of your online behavior is being analyzed behind the scenes. As AI gets smarter, CAPTCHAs will only get weirder, or smarter, or vanish altogether, replaced by systems that silently infer who is human and who is not, without ever asking you to prove it.