By Vishwam Sankaran
Copyright independent
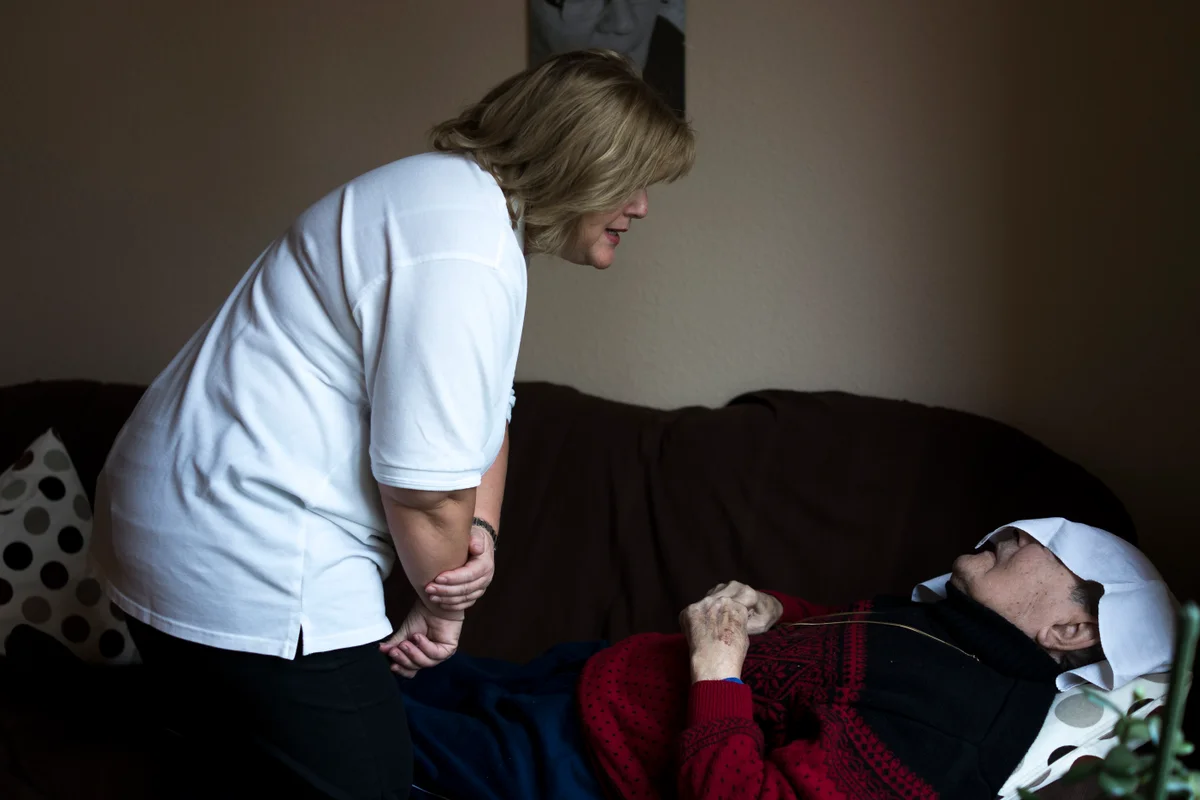

A newly developed system to deliver tiny capsules containing anti-inflammatory proteins to specific parts of the brain may help fight Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases.
AstroCapsules, described in a recent study published in the journal Biomaterials, are small capsules made from a safe gel containing brain cells known as astrocytes
Researchers in many countries are seeking to treat neurodegenerative conditions like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s by restoring the ability of the brain’s immune cells to fight diseases and keep tissues in balance. “Age-related inflammation that is associated with diseases, such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, necessitates targeted anti-inflammatory interventions at region-specific sites,” the new study notes.
When astrocytes, which contribute to the healthy functioning of the brain as part of the immune system, are armed with anti-inflammatory protein IL-1Ra and packed in capsules, they significantly reduce brain inflammation, the study says.
“Encapsulated human astrocytes were able to secrete proteins to the external environment and become reactive in response to stimuli,” the study concluded.
The researchers found that AstroCapsules, each about the size of a large grain of sand, could withstand rejection by the immune system of mice and still function.
“Encapsulated astrocytes were able to be stably implanted into the rodent brain while secreting IL-1Ra,” they said.
Study co-author Robert Krencik from the Houston Methodist Research Institute said that this mechanism solved “several current problems with cell-based therapeutics to the nervous system”.
The system could present a new way to treat debilitating neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
“Encapsulating cells in a way that shields them from immune attack has been a central challenge in the field,” another study author, Omid Veise from Rice University in Texas, noted. “Our hope is that this work will help move cell therapies closer to becoming real treatment options for patients with neurodegenerative disease.”
The researchers are looking to conduct further studies to determine the extent of the anti-inflammatory effect of AstroCapsules.
“This strategy holds promise for the localised delivery of anti-inflammatory agents to the brain across various applications,” they said.