By K Shiva Shanker
Copyright thehindu
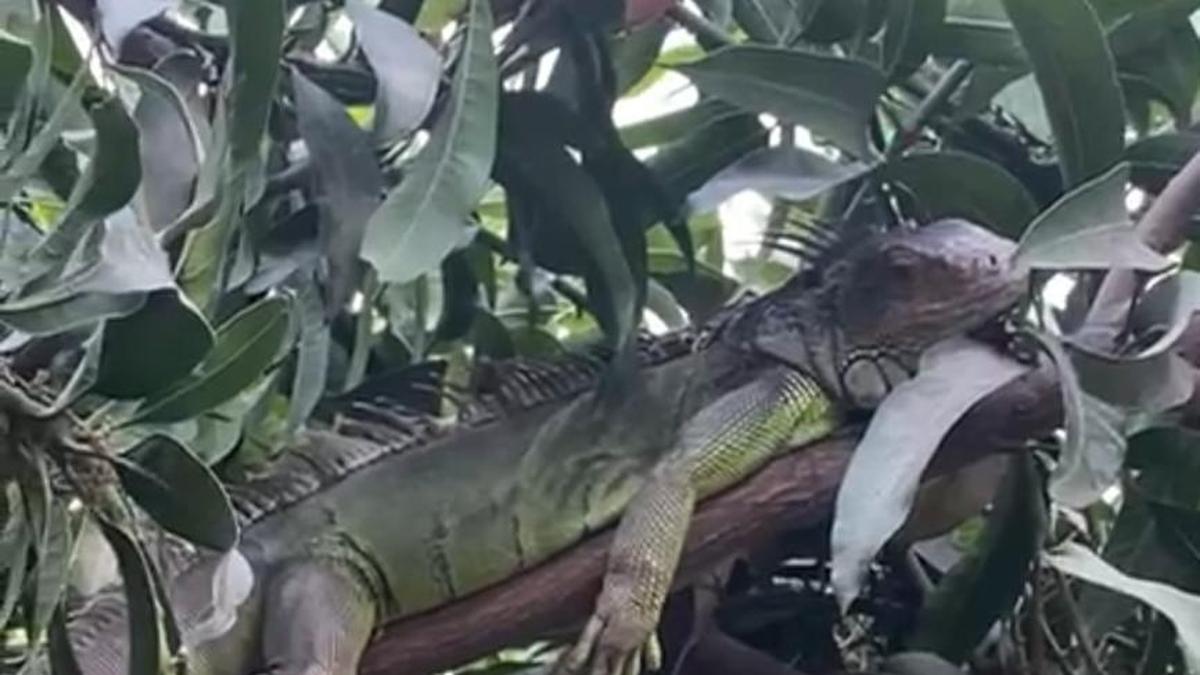

In March last year, volunteers of Friends of Snakes Society rescued a green iguana perched on a mango tree in Dilsukhnagar of Hyderabad. A few days ago, green-keeled lizards and girdled lizards were found in the baggage of two passengers from Bangkok at Hyderabad’s Rajiv Gandhi International Airport. None of them are native species of India.
Experts warn that in the absence of natural predators, the exotic species might thrive and compete with local fauna for resources. Besides, the growing fascination with exotic pets, coupled with neglect of native species, could further threaten indigenous populations. They also note that non-native plants, fish and other organisms are already altering local ecosystems.
Exotic snakes may raise snakebite burden
“Exotic species, when released into the wild, have the potential to disrupt delicate ecological balances by outcompeting or preying on native species. This is particularly problematic as many exotic animals lack natural predators in the Indian ecosystem, allowing them to thrive and multiply unchecked. There have been several documented instances where exotic species, including snakes and reptiles, have escaped from private enclosures or were deliberately released into the wild,” said Avinash Visvanathan, general secretary of FoSS.
He said exotic venomous species could exacerbate the snakebite burden that our country already faces.
Competitive exclusion could drive out local species
Chelemla Srinivasulu, professor of Zoology at Osmania University, Hyderabad, said that native species, which adapt to local habitats over the years, are vulnerable if exotic species adapt better, creating uneven competition for resources. “The competitive exclusion could drive local species to extinction,” said Mr.Srinivasulu.
Water Hyacinth
He said that this applies to other beings too. Water hyacinth was introduced in India in the colonial era for its aesthetic appeal, but turned out to be a problem as they grow fast and cover water bodies. It continues to be an issue even to this day.
Sucker fish
Sucker fish, which is not native to India, was brought in by those in the aquarium business as they clear algae and keep aquariums clean. But they were introduced into water bodies as they do not look pleasant after growing up and now they are spread around in several water bodies here.
The Giant African Land Snails, which posed a problem in agriculture fields in some parts of neighbouring Andhra Pradesh, was recently found in Nizamabad of Telangana, he said. Photographs of it were shared in naturalists’ groups.
To effectively address the growing threat, the government must take stronger action to enforce the new wildlife protection laws. Authorities need to ramp up efforts to curb the illegal trade in exotic species, including stricter penalties for individuals involved in the trafficking of these animals, he said. Increased surveillance of online platforms where the trade is often facilitated is also necessary.