By Contributor,Emil Sayegh
Copyright forbes
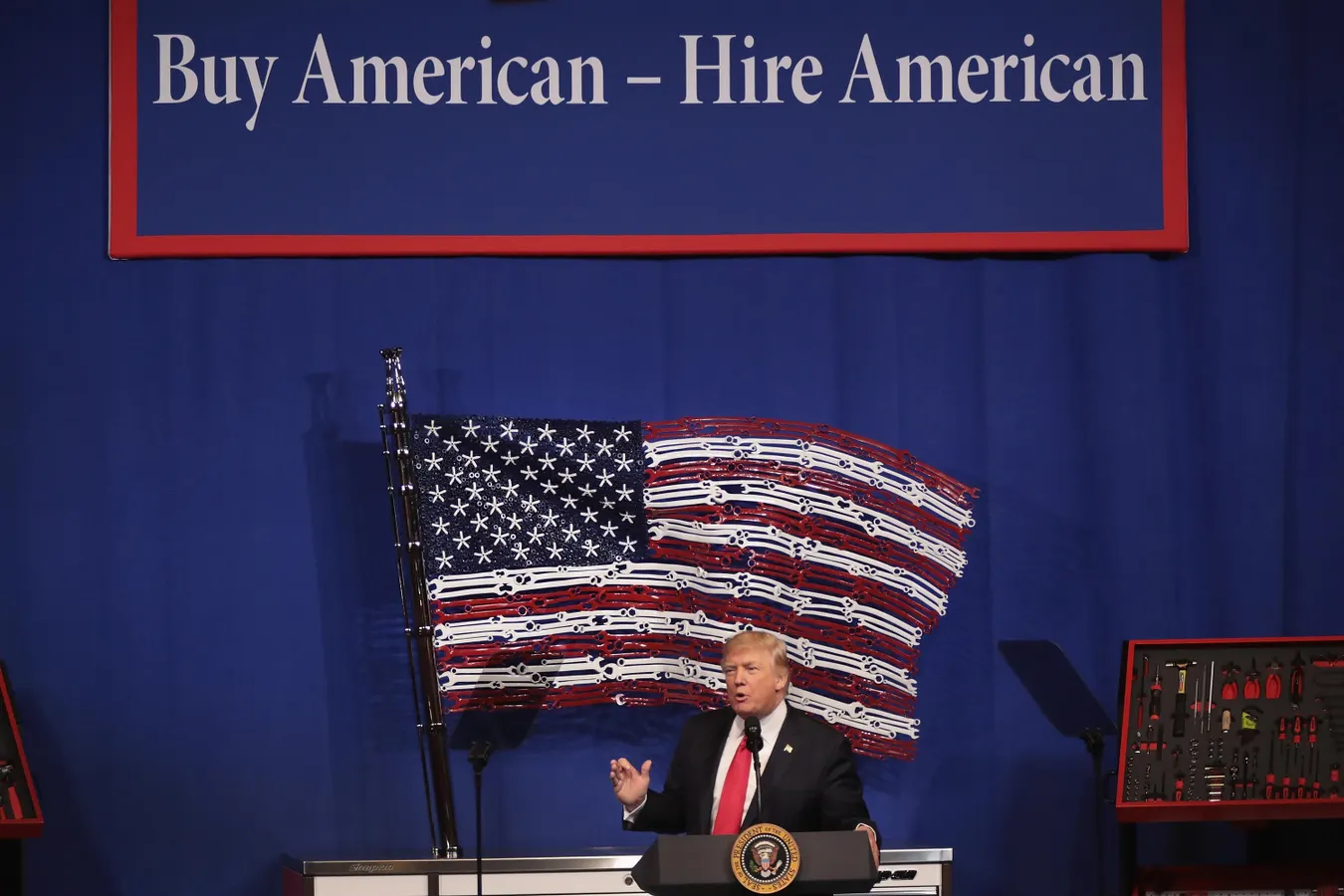

President Donald Trump signs a sudden proclamation on September 19, 2025 imposing a $100,000 fee on new H-1B visa petitions for foreign nationals outside the United States, a move that shocked the tech and cybersecurity industries.
Getty Images
On September 19, 2025 President Donald Trump signed a sudden proclamation called “Restriction on Entry of Certain Nonimmigrant Workers” that no one saw coming. It imposes a $100,000 fee on new H-1B visa petitions for foreign nationals outside the United States. The one time fee does not apply to existing visa holders or renewals. The rule takes effect immediately. It also raises prevailing wage requirements and introduces a national interest exception that allows the Department of Homeland Security to waive the fee in certain cases. The proclamation is set to last 12 months unless extended.
This order represents one of the most dramatic changes to the H-1B visa system in decades. Just like tariffs, everyone overreacted, and this too shall pass. For years companies have paid relatively modest filing fees to sponsor high-skill workers. Now, the cost of a single new petition rivals the salary of an entry-level engineer. The administration says the move is intended to protect U.S. workers, prevent wage suppression and ensure that foreign hires are limited to cases of clear national interest.
The Industry’s Reaction
“This came out of nowhere and could have devastating consequences for America’s innovation engine,” said one Silicon Valley venture capitalist who invests heavily in enterprise startups.
John Trasvina, former general counsel to the U.S. Senate Judiciary Committee, noted that the initial confusion was damaging. “At first people thought existing H-1B holders would be turned away unless employers paid $100,000. Clarification came but the panic was real.”
Indian IT industry body Nasscom also warned of ripple effects on U.S. competitiveness and global job markets, pointing out that many firms rely heavily on rotating skilled foreign labor into U.S. operations.
MORE FOR YOU
While industry leaders focused on disruption and risk, the administration framed the move as a chance to redirect opportunities toward U.S. citizens and strengthen the domestic workforce.
The State Of Tech Unemployment
Microsoft had already announced more than 15,000 layoffs in 2025, including 6,000 in May and another 9,000 in July. Across the broader industry more than 144,900 tech workers have been laid off in over 500 separate events this year according to TrueUp. Meta, Google, Intel and Amazon all contributed heavily to those totals.
While the CompTIA unemployment report shows tech unemployment at 2.8 percent compared to 4.3 percent for the overall U.S. labor force, those percentages mask the scale of disruption. Tens of thousands of highly skilled engineers and cybersecurity professionals remain on the sidelines. This sudden policy shifts the spotlight toward that available domestic workforce.
Federal agencies have also been shrinking as part of efficiency drives tied to DOGE. Agencies like CISA and DHS have already let go of staff. Many of those workers are cleared and trained, yet now find themselves searching for new opportunities. This policy creates pressure and incentive to reabsorb those citizens into both government and private sector cyber roles where they are badly needed.
Mixed Impact On Tech And Cybersecurity
For large technology companies the fee represents a costly inconvenience, but many can absorb it. For startups and mid-sized firms the burden may be crushing. Some may choose to relocate development offshore, an option that creates new risks. Innovation in AI, cloud and advanced data science could slow if fewer foreign graduates enter the U.S. market. Worse, cybersecurity work, such Security Operating Centers moved offshore is a dangerous recipe for the United States. Protecting critical infrastructure and government systems requires U.S. citizens working on U.S. soil. Moving those functions abroad undermines security and invites potential insider threats from hostile actors.
Federal downsizing has already put thousands of cleared cyber professionals out of work. This creates both a problem and an opportunity. On one hand, budget cuts may have weakened agencies responsible for defending critical infrastructure. On the other, the sudden availability of highly trained citizens means private companies now have access to talent that can be integrated into private cyber operations. This policy directly channels employers toward that workforce, strengthening national security by ensuring that sensitive work is handled by Americans.
Why This Could Be Beneficial
The Trump administration views this move as a way to accomplish multiple goals. It forces companies to prioritize U.S. citizens and laid-off federal workers. It raises the cost of relying on foreign labor and discourages abuse of the H-1B system. It strengthens national security by ensuring that cyber roles are staffed by U.S. citizens on U.S. soil where clearance processes are more reliable and insider threats are less likely.
The policy also generates new revenue that can support reskilling programs, STEM education, and veteran transition initiatives. Just as importantly, it aligns with broader efforts like the Cybersecurity Maturity Model Certification, which require defense contractors to meet strict security and compliance standards by November 10, 2025. By prioritizing U.S. workers and cleared personnel, companies can more easily meet CMMC requirements while reducing risk across the defense industrial base.
Risks And The Dual Reality
The risks are equally clear. If retraining programs and certification pathways are not expanded quickly, many open roles will remain unfilled. Startups and immigrant-founded companies could falter or shift overseas. America’s global reputation as the preferred destination for top technical talent could decline. There are also legal questions about whether the executive branch has the authority to impose such sweeping fees and how “national interest exceptions” will be applied.
At the same time, the opportunity is real. Tens of thousands of unemployed U.S. tech and cyber professionals are available and ready. This policy could open doors for them to reenter the workforce at higher wages and with greater stability. Whether this becomes a national advantage or a national setback depends entirely on whether America invests quickly and decisively in training, placement and domestic talent pipelines.
A Policy That Forces A Reckoning
The $100,000 H-1B fee is one of the boldest shifts in high-skill immigration policy in decades. It came without warning and blindsided even the largest players in the industry. The winners will be companies that already rely on U.S. citizens and have strong domestic pipelines. The losers may be startups, global firms dependent on H-1B talent and foreign nationals who had hoped to contribute to the American economy.
At its core this is not just about fees. It is about how America balances innovation, economic growth, and national security. The immediate shock and overreaction mirror what we saw with tariffs in past years. Then, as now, markets and companies panicked, but eventually adapted. The real measure will be whether the United States uses this disruption as a catalyst to train, hire and secure its own workforce, including veterans and employees laid off from governmental agencies, or whether it allows opportunity to slip away.
Editorial StandardsReprints & Permissions